James Webb geimsjónauki (JWST)er pláss observatory designed to conduct infrared astronomy and launched successfully on 25 December 2021 will enable two research teams to study earliest galaxies in the alheimurinn. The research teams will use JWST’s powerful instruments (NIRISS, NIRCam and NIRSpec) to capture and characterize some of the earliest galaxies.
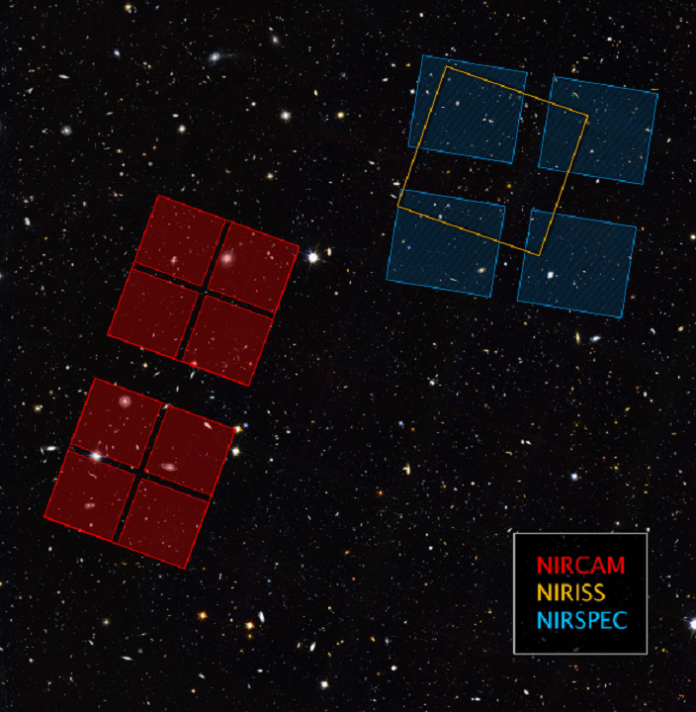
The Next Generation Deep Extragalactic Exploratory Public (NGDEEP) Survey will target Hubble Ultra Deep Field by pointing telescope’s Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) on the primary Hubble Ultra Deep Field and Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) on the parallel field. The two instruments NIRISS and NIRCam will capture infrared light (redshifted due to expansion of alheimurinn). The data will be released immediately to benefit the researchers.
NGDEEP team will also identify metal elements in the early galaxies especially in smaller and dimmer ones that haven’t yet been thoroughly studied so far. Study of metal contents of galaxies is standard way to trace evolution across cosmic time. There were only hydrogen and helium in the beginning of the alheimurinn. New elements were formed by successive generations of stjörnur. Studying metal contents of galaxies will help to plot out precisely when various elements existed and update models that project how galaxies evolved in the early alheimurinn.
The other research team will examine the primary Hubble Ultra Deep Field using the microshutter array within the telescope’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec). This will provide first large sample of earliest galaxies that existed in the early alheimurinn enabling researchers to understand them in detail.
The story of study of snemma alheimsins began in 1995 with the decision to focus Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on nothing in the hitherto unexplored field in the sky. Hubble captured about 3000 images of galaxies at different stages of stellar evolution. Better known as Hubble Deep Field, these images were first pictures of early galaxies and revolutionised the field of astronomy.
As a successor of Hubble pláss telescope (HST), James Webb geimsjónauki (JWST) is carrying forward the Hubble telescope’s legacy in the area of study of early alheimurinn. Webb telescope aims to search for light from the first stjörnur and galaxies that formed in the Universe after the Big Bang to study the formation and evolution of galaxies, to understand the formation of stjörnur og Planetary systems and to study Planetary systems and the origins of life.
Snemma alheimurinn in the first several hundred million years after the big bang was a very different place. It was semi-opaque. This is when the first galaxies in the alheimurinn were beginning to form. Many distant galaxies have been spotted by the telescopes but none earlier than 400 million years after the big bang. What were galaxies that existed even earlier like? The above mentioned, two research teams will answer just this by revealing details of the earliest chapters of Galaxy þróun.
***
Heimildir:
- NASA 2022. NASA's Webb to Uncover Riches of the Early Universe, Gefið út 22. júní 2022. Aðgengilegt á netinu á https://webbtelescope.org/contents/news-releases/2022/news-2022-015.html Skoðað 23. júní 2022.
- Prasad U., 2021. James Webb geimsjónauki (JWST): Fyrsta geimstjörnustöðin tileinkuð rannsóknum á alheiminum snemma. Vísindaleg Evrópu. Birt 6. nóvember 2021. Aðgengilegt á netinu á http://scientificeuropean.co.uk/sciences/space/james-webb-space-telescope-jwst-the-first-space-observatory-dedicated-to-the-study-of-early-universe/
***